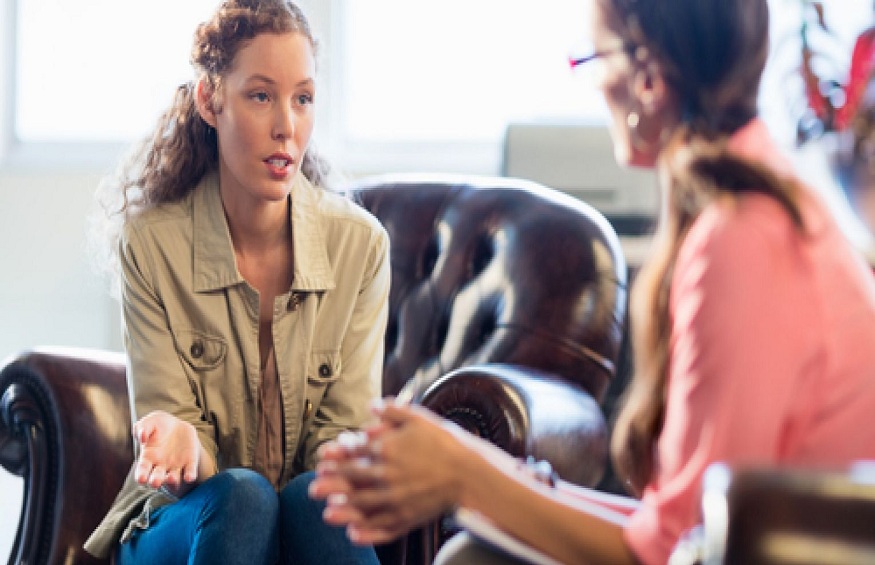
In the realm of mental health treatment, various therapeutic approaches have emerged, each offering unique methods to alleviate psychological distress and promote well-being. Among these approaches, Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) has gained significant recognition and popularity for its effectiveness in addressing a wide range of mental health concerns.
This blog post aims to provide an in-depth analysis of CBT, exploring its key principles, techniques, and applications in the field of psychology.
Understanding Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy is a psychotherapeutic approach that combines cognitive and behavioural strategies to address psychological issues. Developed by Aaron T. Beck in the 1960s, CBT is based on the premise that our thoughts, emotions, and behaviours are interconnected and influence one another. By identifying and modifying maladaptive patterns of thinking and behaving, individuals can experience positive changes in their emotions and overall well-being.
Key Principles of CBT
Cognitive Restructuring: CBT emphasizes identifying and challenging irrational or negative thoughts, known as cognitive distortions. Through cognitive restructuring, individuals learn to replace these unhelpful thoughts with more realistic and positive alternatives. This process helps to reduce emotional distress and improve coping mechanisms.
Behavioural Activation: CBT recognizes the role of behaviour in maintaining psychological difficulties. Behavioural activation focuses on identifying and modifying problematic behaviours that contribute to distress. By engaging in activities that bring a sense of pleasure or accomplishment, individuals can break the cycle of negative thinking and improve their mood.
Skill-Building: CBT equips individuals with practical skills and techniques to manage their thoughts, emotions, and behaviours more effectively. These skills include relaxation techniques, problem-solving strategies, assertiveness training, and stress management, among others. By developing these skills, individuals become more empowered in handling challenges and maintaining their mental well-being.
Techniques Used in CBT
Socratic Questioning: This technique involves asking probing questions to help individuals identify and evaluate their thoughts and beliefs. By challenging automatic negative thoughts, individuals gain a more balanced and rational perspective on their experiences.
Exposure Therapy: Particularly effective for anxiety disorders, exposure therapy gradually exposes individuals to feared situations or objects in a safe and controlled environment. Through repeated exposures, individuals learn that their fears are unfounded, leading to a reduction in anxiety.
Behavioural Experiments: This technique involves testing the validity of one’s beliefs through experimentation. By engaging in new behaviours or challenging previously held assumptions, individuals can gather evidence that contradicts their negative thoughts and beliefs.
Applications of CBT
CBT has proven to be highly effective in treating a wide range of mental health conditions, including:
Anxiety Disorders: CBT has been extensively used in the treatment of anxiety disorders such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, and specific phobias. It helps individuals identify and challenge irrational thoughts and develop coping mechanisms to manage anxiety.
Depression: CBT is considered one of the most effective treatments for depression. By addressing negative thinking patterns and helping individuals engage in positive behaviours, CBT can alleviate depressive symptoms and prevent relapse.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): CBT, particularly trauma-focused CBT, has been successful in treating PTSD. It focuses on processing traumatic experiences, challenging distorted beliefs, and developing healthy coping strategies.
Substance Use Disorders: CBT plays a vital role in the treatment of substance use disorders by addressing the underlying thoughts, beliefs, and behaviours associated with addiction. It helps individuals develop skills to resist cravings, cope with triggers, and prevent relapse.
Conclusion
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) has become a cornerstone in the field of mental health treatment due to its evidence-based approach and successful outcomes. By addressing the interplay between thoughts, emotions, and behaviours, CBT empowers individuals to recognize and modify maladaptive patterns, leading to improved mental well-being. Whether used to treat anxiety, depression, trauma, or addiction, CBT provides a versatile and effective therapeutic framework that continues to transform the lives of many.












+ There are no comments
Add yours